Forex Broker Regulations in India: A Comprehensive Guide
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has become increasingly popular in India. However, navigating the world of Forex trading requires a clear understanding of the regulatory framework that governs Forex brokers in the country. In this blog, we’ll explore the key aspects of Forex broker regulations in India, the authorities involved, and what traders need to know to ensure a safe and legal trading experience[1].
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape
India’s Forex market operates under a well-defined regulatory framework. The primary regulatory body overseeing Forex trading in India is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), with additional oversight from the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). These authorities work to ensure that the Forex market functions smoothly and that traders are protected from fraudulent activities.
1. Role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
The Reserve Bank of India plays a pivotal role in regulating Forex trading in India. The RBI primarily focuses on maintaining the stability of the country’s foreign exchange reserves and ensuring that all Forex transactions comply with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999.
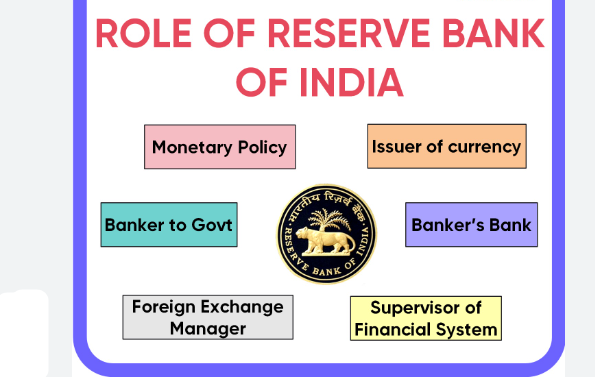
Key Functions of RBI in Forex Regulation:
- Authorization of Forex Brokers: The RBI authorizes entities to operate as Forex brokers in India. These brokers must adhere to strict guidelines and maintain transparency in their operations.
- Permitted Currency Pairs: Under the RBI’s regulations, Indian residents can only trade currency pairs[2] that include the Indian Rupee (INR). The permitted pairs are INR/USD, INR/EUR, INR/GBP, and INR/JPY.
- Capital Controls: The RBI imposes capital controls to limit the amount of foreign exchange that can be transacted by individuals and businesses, ensuring that the country’s foreign reserves are not depleted.
2. Role of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
While the RBI focuses on the macroeconomic aspects of Forex trading, SEBI’s role is to protect investors and ensure fair market practices. SEBI regulates Forex trading as part of the broader securities market in India.
Key Functions of SEBI in Forex Regulation:
- Licensing of Brokers: SEBI issues licenses to brokers who wish to offer Forex trading services in India. Only brokers registered with SEBI are legally allowed to provide these services.
- Compliance and Reporting: SEBI requires brokers to comply with stringent reporting and transparency standards. This includes regular audits and disclosure of financial information.
- Investor Protection: SEBI has implemented various measures to protect retail traders[3], such as ensuring that brokers offer fair prices, execute trades efficiently, and provide adequate risk warnings.
3. Legal Framework for Forex broker regulations India
The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999 governs Forex trading in India. This legislation replaced the earlier Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) and aimed to facilitate external trade and payments while maintaining the country’s foreign exchange market stability.
Key Provisions of FEMA:
- Permitted Transactions: FEMA defines which foreign exchange transactions are permitted and which are restricted. For instance, the regulations prohibit Indian residents from engaging in speculative trading in Forex (trading for profit without underlying exposure).
- Currency Derivatives: Under FEMA, Indian residents can trade in currency derivatives[4] on recognized exchanges such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). These derivatives must involve the INR as one of the currencies in the pair[5].
- Offshore Trading Restrictions: Indian residents are prohibited from trading in Forex pairs that do not involve the INR through offshore brokers. This is to prevent capital flight and protect the country’s foreign exchange reserves.
4. Choosing a Regulated Forex Broker in India
Given the strict regulatory environment, it is crucial for traders to choose a Forex broker that is fully compliant with Indian regulations. Here are some key factors to consider:

SEBI Registration:
- Ensure that the broker is registered with SEBI. This can be verified on SEBI’s official website, where a list of authorized brokers is maintained.
Transparency:
- A regulated broker must maintain transparency in their operations, including clear disclosure of fees, spreads, and other costs. They should also provide accurate market data and execute trades efficiently.
Safety of Funds:
- SEBI-regulated brokers must segregate client funds from their own operating capital. This practice protects your funds even if the broker faces financial difficulties.
Customer Support:
- Regulated brokers must provide adequate customer support to assist traders with their queries and issues. This includes offering support in local languages and providing clear information on trading procedures and risks.
Trading Platforms:
- SEBI-regulated brokers must typically offer trading platforms that are reliable, secure, and user-friendly. These platforms should also comply with SEBI’s technical standards.
5. The Risks of Trading with Unregulated Brokers
Although regulations govern the Forex market in India, traders still face risks when they use unregulated or offshore brokers.These brokers often operate outside the purview of Indian regulators and may not adhere to the same standards of transparency and client protection.
Risks Involved:
- Lack of Legal Recourse: If you face issues with an unregulated broker, such as withdrawal problems or unfair trading practices, you may have limited or no legal recourse in India.
- Higher Risk of Fraud: Unregulated brokers are more likely to engage in fraudulent activities, such as manipulating prices or refusing to process withdrawals.
- Penalties for Offshore Trading: Trading through offshore brokers that offer non-INR currency pairs can lead to penalties from Indian authorities under FEMA.
6. Compliance Requirements for Forex Traders
In addition to choosing a regulated broker, Forex traders in India must adhere to certain compliance requirements to ensure that their trading activities are legal.
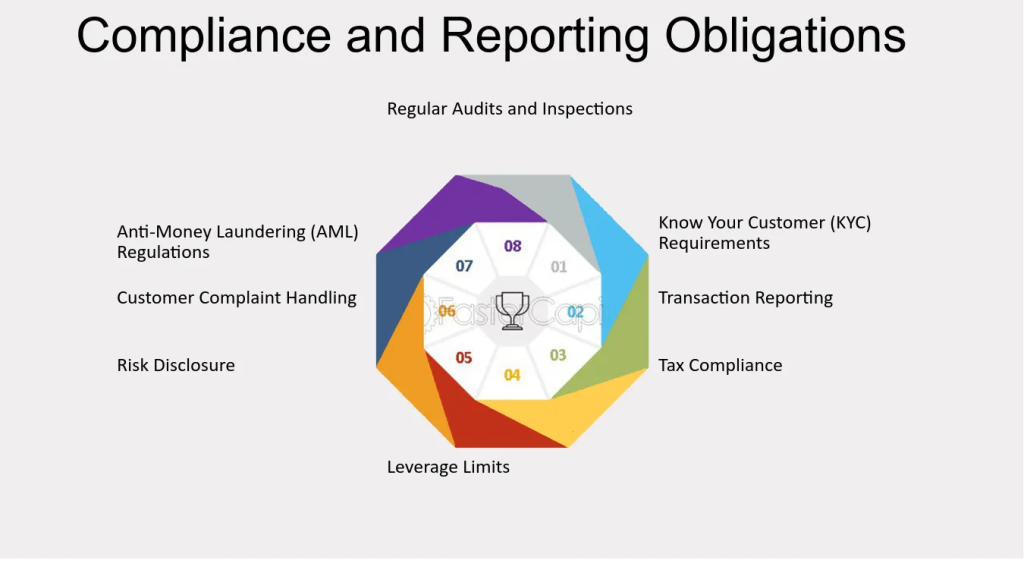
Compliance Tips:
- Trade Only Permitted Pairs: Stick to trading currency pairs that involve the INR, as trading in non-INR pairs through offshore platforms is illegal for Indian residents.
- Use SEBI-approved brokers: Ensure that SEBI authorizes your broker and that the broker complies with all relevant regulations.
- Report Your Earnings: Forex trading profits are subject to taxation in India. Ensure that you report your earnings accurately when filing your income tax returns.
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on the latest regulations and guidelines issued by the RBI and SEBI to avoid any unintentional violations.
Conclusion
Forex trading in India operates under a robust regulatory framework designed to protect traders and maintain the stability of the country’s financial markets. By choosing a SEBI-regulated broker and also adhering to the guidelines set forth by the RBI and FEMA, traders can engage in Forex trading legally and safely. Understanding the regulatory environment is crucial for anyone looking to participate in the Forex market, as it not only ensures compliance but also helps in making informed trading decisions.
Forex broker regulations India FAQs
Are Forex brokers regulated in India?
A: Yes, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulate Forex brokers in
India.
These regulatory bodies ensure that brokers operate within legal guidelines to protect traders.
What currency pairs can be traded legally in India?
A: In
India, traders can legally trade currency pairs that include the Indian Rupee (INR).
This includes pairs like USD/INR, EUR/INR, GBP/INR, and JPY/INR.
Can Indian residents trade on international Forex
platforms?
A: No, Forex trading on international
platforms that offer currency pairs not involving INR is not
allowed for Indian residents. They must use platforms regulated in India and trade
permissible currency pairs.
What is the role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in Forex
trading?
A: The RBI oversees all foreign exchange transactions in
India. It sets guidelines and regulations to ensure the stability and integrity of
the Indian financial system, including the Forex market.
How does SEBI regulate Forex brokers in India?
A: SEBI
regulates Forex brokers by ensuring they comply with financial regulations, maintain
transparency, and
