Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, has gained significant popularity worldwide as a potentially lucrative investment opportunity. However, stringent rules and regulations set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) govern the landscape of forex trading in India. These rules are in place to safeguard Indian investors from the inherent risks associated with forex trading while ensuring that the country’s financial system remains stable.
1. Understanding Forex Trading
Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currencies in the global market. Traders seek to capitalize on the variations in currency exchange rates to earn a profit. For example, if a trader believes that the Euro will strengthen against the US Dollar, they might buy Euros with US Dollars and later sell them at a higher rate, thus making a profit.
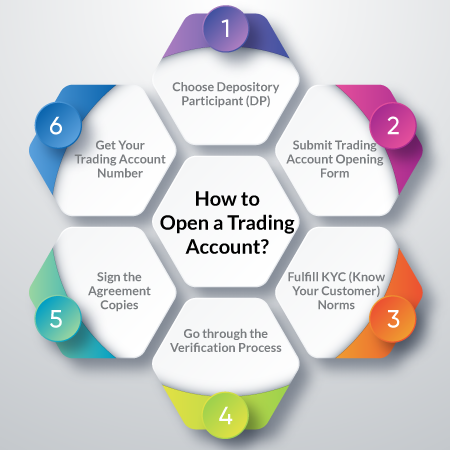
2. Regulatory Authorities in India
In India, forex trading is regulated primarily by two authorities:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The RBI oversees all foreign exchange transactions in the country, ensuring compliance with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) of 1999.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): SEBI regulates the financial markets in India, including forex trading, to protect the interests of investors.
3. Permissible Currency Pairs
One of the most crucial rules for forex trading in India is that trading is only allowed in certain currency pairs[1]. As per RBI guidelines, Indian traders can trade in forex pairs[2] that include the Indian Rupee (INR). The following pairs are permitted:
- USD/INR
- EUR/INR
- GBP/INR
- JPY/INR
Indian residents are strictly prohibited from trading in any other currency pairs unless[3] they do so on recognized exchanges under specific schemes.
4. Trading Platforms and Exchanges
Forex trading in India can only be conducted on authorized platforms. SEBI-approved exchanges such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), and Metropolitan Stock Exchange (MSE) offer currency derivatives trading. These platforms ensure that traders carry out transactions within the legal framework set by Indian regulators.
5. Leverage and Margin Requirements
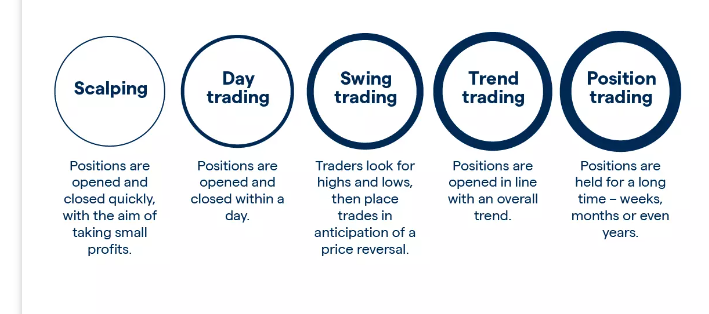
6. Taxation on Forex Trading
Profits earned from forex trading in India are subject to taxation. Income from forex trading is categorized under “Income from Other Sources” and is taxed according to the individual’s income tax slab. Additionally, the Securities Transaction Tax (STT) may apply to certain forex transactions carried out on recognized exchanges.
7. Risks and Precautions
Forex trading carries a high level of risk because of the unpredictable nature of currency markets. Indian traders should exercise caution and make sure they are well-informed before engaging in forex trading.It is advisable to start with a demo account to gain experience and understand the market dynamics. Furthermore, traders should only invest what they can afford to lose and should use risk management tools such as stop-loss orders to mitigate potential losses.
8. Illegal Forex Trading Activities
It is important to note that online forex trading through foreign brokers is illegal in India. Many websites offer forex trading services to Indian residents, but these platforms operate outside the jurisdiction of Indian authorities. Engaging in such activities can lead to severe penalties, including legal action. Indian traders should only use SEBI-regulated platforms to ensure they are trading within the law.
9. Conclusion
Forex trading in India is subject to strict regulations to protect investors and maintain the stability of the financial system. By adhering to the guidelines set by the RBI and SEBI, traders can engage in forex trading within a legal and safe framework. It is essential for traders to stay informed about the rules and continuously educate themselves about the risks involved in forex trading.
FAQs on Forex Trading Rules in India
1. Is forex trading legal in India?
2. Which currency pairs are allowed for trading in India?
Indian regulators allow traders to trade only in the following currency pairs: USD/INR, EUR/INR, GBP/INR, and JPY/INR. Traders may only trade in other currency pairs[4] on recognized exchanges under specific schemes.
3. Can I trade forex through international brokers?
No, trading forex through international brokers is illegal for Indian residents. Forex trading must be conducted through SEBI-regulated platforms and exchanges within India to ensure compliance with Indian laws.
4. What are the leverage limits for forex trading in India?
Leverage in forex trading in India is typically lower compared to international standards, with most brokers offering leverage between 10:1 and 50:1, depending on the currency pair[5] and market conditions.
5. How is forex trading income taxed in India?
The tax authorities classify profits from forex trading in India under “Income from Other Sources” and tax them according to the individual’s income tax slab. Additionally, certain transactions might be subject to the Securities Transaction Tax (STT).
