The foreign exchange market, commonly known as the forex or FX market[1], is a global marketplace for trading currencies. As the largest and most liquid market in the world, it offers significant opportunities for investors and businesses alike. In India, the forex market has been gaining traction, driven by the country’s increasing integration with the global economy[1]. This blog delves into the nuances of the forex market in India, exploring its opportunities, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding the Forex Market
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is decentralized, meaning that there is no central exchange. Instead, trading takes place over-the-counter (OTC) through a global network of banks, financial institutions, and individual traders. Currencies[2] are traded in pairs, with the value of one currency being quoted against another. Major currency pairs involve the US dollar, while minor pairs consist of other strong currencies like the Euro, Yen, and Pound.
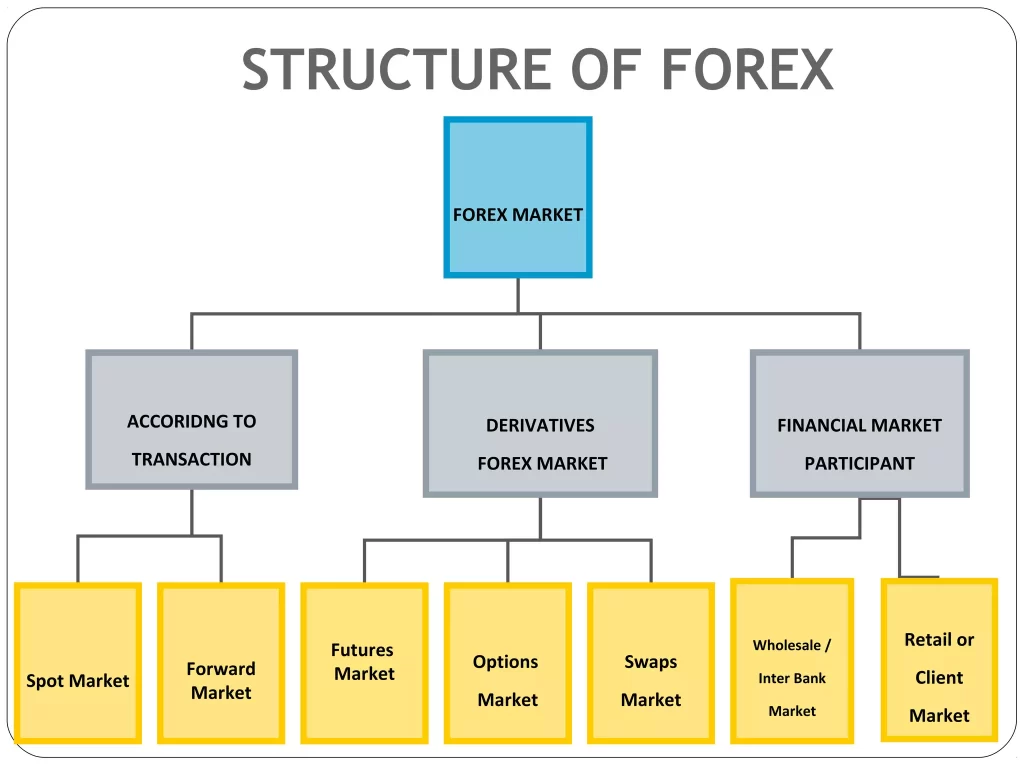
Structure of the Indian Forex Market
The Indian forex market is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)[2], which, in turn, ensures both stability and the smooth functioning of the market. Consequently, the main participants in this market include not only commercial banks but also financial institutions, corporates, and retail traders. The market comprises two segments: the spot market and the derivatives market[3], which includes futures, options, and swaps.
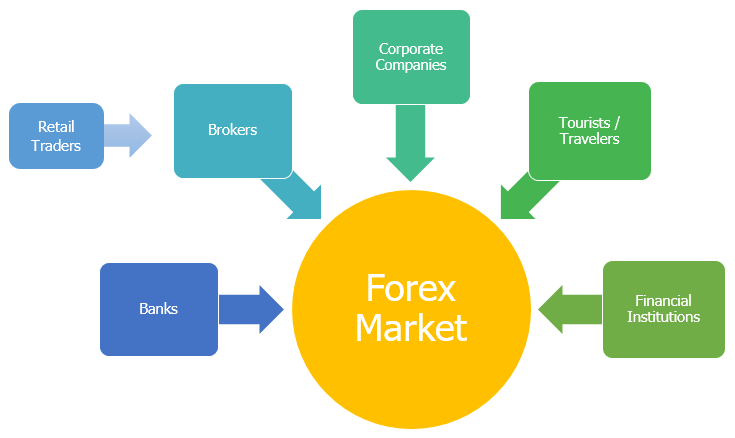
Key Participants
- Commercial Banks: These are the primary players, facilitating most of the forex transactions in India. They provide various forex-related services such as currency conversion, forward contracts, and hedging solutions.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The central bank regulates and oversees the forex market, ensuring compliance with foreign exchange regulations and maintaining currency stability[4].
- Corporates and Importers/Exporters: Businesses engaged in international trade participate in the forex market to hedge against currency risks and manage their foreign exchange requirements.
- Retail Traders: With advancements in technology and the availability of online trading platforms, individual traders have also started participating in the forex market, seeking to profit from currency fluctuations.
Opportunities in the Indian Forex Market
1. Hedging Against Currency Risk
For businesses involved in international trade, the forex market provides an essential tool for hedging against currency risk. Specifically, by entering into forward contracts or options, companies can effectively lock in exchange rates for future transactions. As a result, they protect themselves from adverse currency movements and thereby mitigate potential financial risks.
2. Investment Opportunities
The forex market offers significant investment opportunities for both retail traders and institutional investors. Indeed, with its high liquidity and the potential for substantial returns, many investors are naturally drawn to forex trading. Consequently, the market continues to attract a diverse range of participants seeking to capitalize on these opportunities. Moreover, the availability of leverage allows traders to control large positions with relatively small capital.
3. Arbitrage Opportunities
Arbitrage entails taking advantage of price discrepancies between various markets or financial instruments.
4. Diversification
Investing in the forex market allows for diversification of an investment portfolio. Since currency movements are influenced by a variety of factors, including economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment, forex trading can provide a hedge against other investments such as stocks and bonds.
Challenges in the Indian Forex Market
1. Regulatory Restrictions
The RBI imposes several restrictions on forex trading to ensure market stability and prevent speculative excesses. These regulations can limit the scope and flexibility of forex trading, particularly for retail traders. For instance, margin trading and certain types of derivative contracts may be restricted.
2. Market Volatility
The forex market is known for its high volatility, with currency prices often experiencing significant fluctuations within short periods. While this volatility can create opportunities for profit, it also increases the risk of substantial losses.
3. Lack of Awareness and Education
Despite the growing interest in forex trading, there is still a lack of awareness and education among retail investors in India. Many traders enter the market without adequate knowledge or understanding of the risks involved, leading to poor decision-making and potential financial losses.
4. Technological and Infrastructure Constraints
Access to reliable and advanced trading platforms is crucial for successful forex trading. In India, technological and infrastructure constraints, such as inconsistent internet connectivity and limited access to sophisticated trading tools, can pose challenges for traders.
Future Prospects of the Indian Forex Market
1. Technological Advancements
The advent of fintech and digital platforms is expected to revolutionize the Indian forex market. With the proliferation of online trading platforms, mobile apps, and algorithmic trading systems[5], market participants can expect enhanced accessibility, efficiency, and transparency in forex trading.
2. Regulatory Reforms
As the Indian economy continues to integrate with global markets, regulatory reforms aimed at liberalizing the forex market are likely. Easing of restrictions on margin trading, introduction of new derivative instruments, and streamlined regulatory processes can attract more participants and boost market liquidity.
3. Increased Retail Participation
With growing awareness and education about forex trading, the participation of retail investors is expected to increase. Educational initiatives, workshops, and online courses can empower retail traders with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the forex market effectively.
4. Integration with Global Markets
India’s increasing integration with the global economy is likely to drive growth in the forex market. As cross-border trade and investment flows expand, the demand for forex services and products will rise, providing opportunities for market players to capitalize on these trends.
5. Development of New Products
The development of new financial products tailored to the needs of different market participants can enhance the depth and breadth of the forex market. Innovative instruments such as currency ETFs, digital currencies, and blockchain-based forex platforms can offer new avenues for trading and investment.
Conclusion
The forex market in India presents a dynamic and evolving landscape, offering a multitude of opportunities for businesses and investors. While regulatory constraints and market volatility pose challenges, the potential for growth and development remains significant. As technological advancements and regulatory reforms continue to shape the market, participants can look forward to a more accessible, efficient, and vibrant forex trading environment in India. For those willing to invest time in learning and understanding the intricacies of forex trading, the Indian forex market holds promise as a lucrative and rewarding arena.
FAQs
1. What is the forex market?
The forex market, often referred to as the currency exchange market, is a worldwide arena where different currencies.It operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and involves the exchange of one currency for another at an agreed-upon price.
2. Who regulates the forex market in India?
The forex market in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which oversees the market to ensure its stability and compliance with foreign exchange regulations.
3. Who are the main participants in the Indian forex market?
The main participants include commercial banks, financial institutions, corporations involved in international trade, and retail traders.
4. What are the primary opportunities in the Indian forex market?
Opportunities include hedging against currency risk, investment prospects, arbitrage opportunities, and portfolio diversification.
5. What are the common challenges faced in the Indian forex market?
Challenges include regulatory restrictions, market volatility, lack of awareness and education among traders, and technological and infrastructure constraints.
